Why does is not work for us?
You are not alone. Experts estimate that one in six couples stays childless involuntarily. As a consequence of a changing society, family planning has changed: The preference of a successful career results in an average age of 30 for women having their first child and it is still rising. Yet, from the 30th year of life onwards, women’s fertility declines. Environmental effects and a job add to that effect.
What might be the problem?
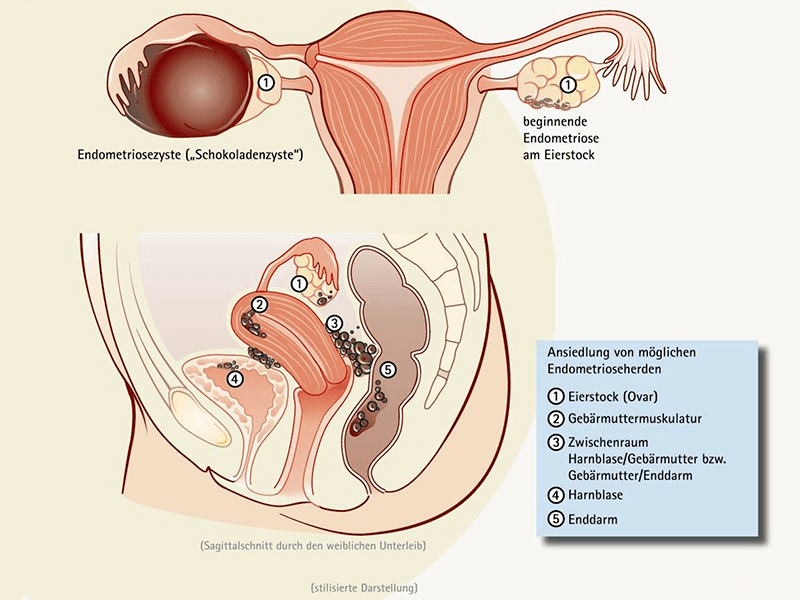
Infertility is defined as the failure of conceiving a child after one year of unprotected intercourse. The reasons for that may lie with both partners. For women, the reasons first in line are tubal ligation, hormonal imbalance and endometriosis.
For men, the quality of sperm cells is decisive for successful conception.
At times, there are no identifiable causes for infertility with either the man or the woman. This phenomenon is called idiopathic infertility.